The Reverse Statement expert in GExperts has received a major upgrade. Previously, it could reverse simple assignments and swap a small set of hardcoded function pairs. Now it uses configurable regex-based rules that you can customize to match your own coding patterns.
What Does Reverse Statement Do?
When you press Alt+Shift+R in the Delphi IDE, the Reverse Statement expert transforms the current line (or selected lines). It tries three types of reversals in order:
- For loop direction – swaps
to/downtoand the loop bounds - Regex-based function rules – applies pattern matching to swap function calls
- Simple assignment – swaps left and right side of
:=
For example:
// For loop reversal for i := 0 to 99 do // becomes: for i := 99 downto 0 do // Function pair reversal Name := StrToInt(Edit1.Text); // becomes: Edit1.Text := IntToStr(Name); // Simple assignment reversal Foo := Bar; // becomes: Bar := Foo;
What’s New: Regex-Based Rules
The old implementation had a small number of function pairs hardcoded in the source. You couldn’t add your own pairs without modifying the GExperts source code. The new implementation replaces this with a list of regex match/replace rules that you can edit in a configuration dialog.
Each rule consists of a match pattern (a regular expression) and a replacement template (using $1, $2, … backreferences). When a line matches a pattern, the replacement produces the reversed version.
Default Rules
GExperts ships with 14 default rules covering common Delphi patterns.
Type conversion pairs (7 rules) handle functions like:
// IntToStr / StrToInt Name := IntToStr(Value); // becomes: Value := StrToInt(Name); // FloatToStr / StrToFloat Text := FloatToStr(Amount); // becomes: Amount := StrToFloat(Text); // Also: BoolToStr/StrToBool, DateToStr/StrToDate, // DateTimeToStr/StrToDateTime, TimeToStr/StrToTime, // CurrToStr/StrToCurr
Registry/INI read/write pairs (7 rules) handle three-parameter Read/Write calls:
// ReadString / WriteString
Name := Reg.ReadString('Section', 'Key', '');
// becomes:
Reg.WriteString('Section', 'Key', Name);
// ReadInteger / WriteInteger
Count := Reg.ReadInteger('Section', 'Key', 0);
// becomes:
Reg.WriteInteger('Section', 'Key', Count);
// Also: ReadBool/WriteBool, ReadFloat/WriteFloat,
// ReadDate/WriteDate, ReadDateTime/WriteDateTime,
// ReadTime/WriteTime
Each pair generates two rules (one for each direction), so the expert can reverse in both directions.
The Configuration Dialog
Open the configuration from the GExperts Configuration dialog under Editor Experts. The new dialog shows all rules in a two-column grid:
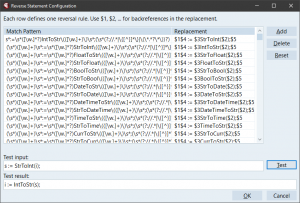
- Match Pattern column – the regex that identifies the statement to reverse
- Replacement column – the template that produces the reversed statement
The toolbar buttons let you:
- Add – add a new empty rule row
- Delete – remove the selected rule
- Reset – restore the default rules
At the bottom of the dialog, a Test section lets you type a sample statement and immediately see what the rules produce – invaluable for developing and debugging your custom regex patterns.
The dialog validates all patterns when you click OK. If a regex has a syntax error, it highlights the problematic row and shows the error message.
Writing Your Own Rules
To add a custom rule, you need to understand the pattern format. Here is a simplified example for a hypothetical Encrypt/Decrypt pair:
The match pattern for Encrypt to Decrypt:
(\s*)([\w.]+)\s*:=\s*([\w.]*?)Encrypt\(([\w.]+)\)\s*;(\s*(?://.*|\{[^}]*\}|\(\*.*?\*\))?)
The replacement:
$1$4 := $3Decrypt($2);$5
The capture groups are:
$1– leading whitespace (preserved for indentation)$2– the left-hand side variable$3– optional object prefix (e.g.,Crypto.)$4– the function argument$5– optional trailing comment
So Result := Crypto.Encrypt(PlainText); becomes PlainText := Crypto.Decrypt(Result);.
You would add a second rule with Encrypt and Decrypt swapped to handle reversal in the other direction.
Tip: Use the Test button in the configuration dialog to verify your patterns before committing them. The argument capture groups use [\w.]+ (identifiers and dots only) rather than arbitrary expressions, because the swapped result must be a valid assignment target.
Availability
This enhancement is available in GExperts 1.3.27 (currently in development). The Reverse Statement expert works in all supported Delphi versions from Delphi 6 through RAD Studio 13.0.
As usual, if you want to try this before the next official release, you can compile your own DLL.
Discussion about this in the corresponding post in the international Delphi Praxis forum.